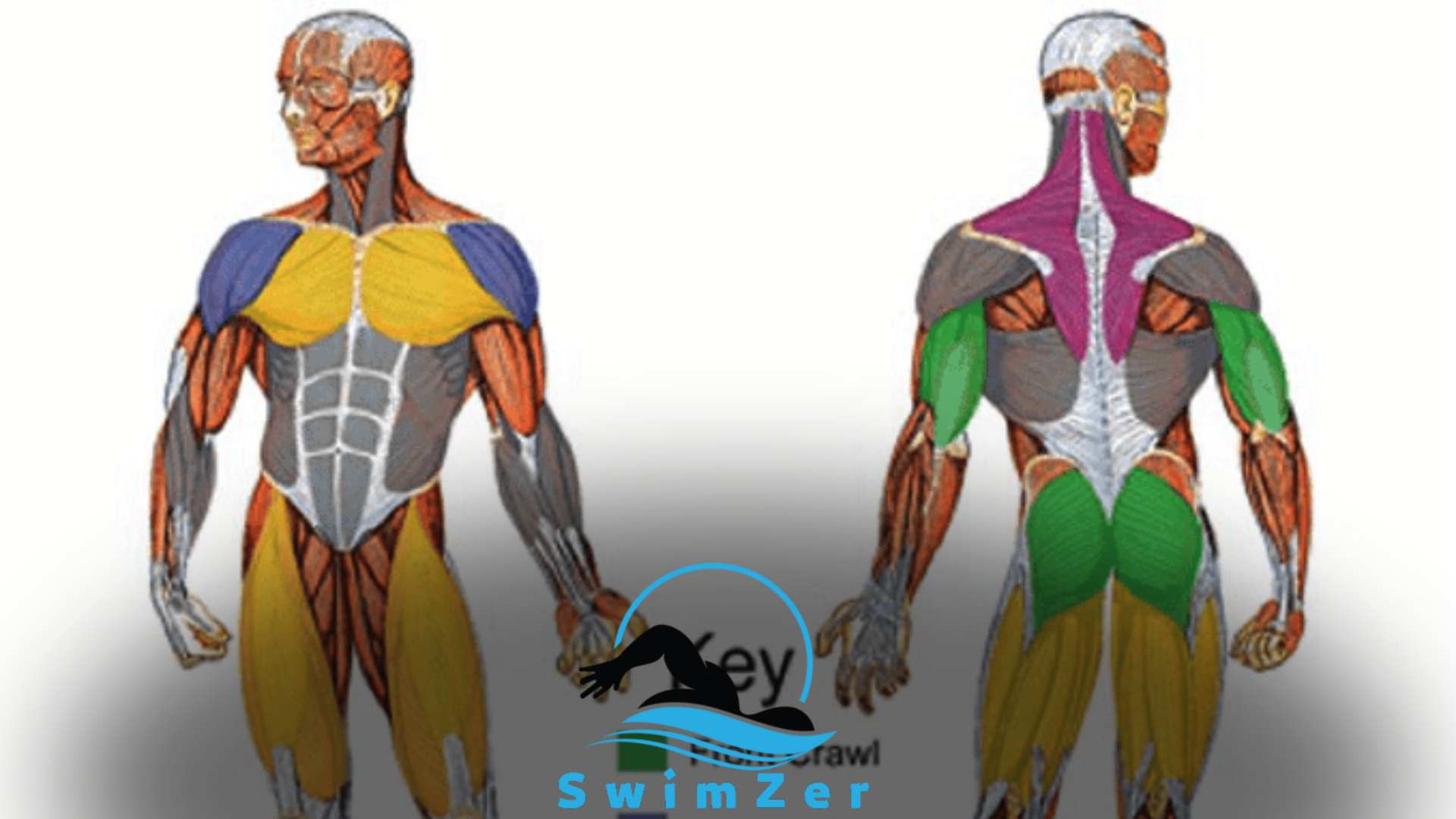
The muscles used when swimming include the core, back, shoulder, and leg muscles. Swimming is a highly effective whole-body workout that engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, providing a great cardiovascular and strength training exercise.
It primarily targets the muscles in the upper body, including the latissimus dorsi, deltoids, trapezius, and pectorals, as well as the abdominal muscles, glutes, quads, and hamstrings.
Continuous movement in the water requires muscle contraction and extension, strengthening and toning the muscles while improving overall flexibility and endurance.
Whether it’s freestyle, backstroke, breaststroke, or butterfly, swimming engages various muscle groups, making it a versatile and effective form of exercise for strengthening the entire body.
Muscles Involved in Swimming
Swimming is a full-body exercise that engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously. The major muscles involved include the arms, shoulders, back, core, and legs.
The arms and shoulders are essential for propulsion and pulling movements through the water. The back muscles are crucial in maintaining proper body position and stability.
The core muscles, including the abdominals and obliques, help to stabilize the body and maintain balance in the water. Lastly, the leg muscles, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves, contribute to kicking movements and provide additional power.
Coordination and balance are vital in swimming as they ensure efficient movement through the water and help minimize drag.
By engaging these muscle groups and focusing on coordination and balance, swimmers can achieve better efficiency and enhance their overall performance in the water.
Understanding the muscles activated during swimming provides insight into the sport’s fitness benefits. Dive deeper into the physical fitness components of swimming to grasp its comprehensive health advantages.
Upper Body Muscles
Swimming engages various upper body muscles, including arms and shoulders. The chest muscles play a crucial role in swimming by aiding in arm extension and pulling through the water.
Strengthening the chest muscles can improve stroke power and efficiency.
Meanwhile, the back muscles provide stability and control during swimming movements. Focusing on exercises that target the back muscles can lead to better body positioning and overall performance in the water.
Swimming is a full-body workout that utilizes multiple muscle groups, so it’s important to strengthen and engage all these muscles to optimize your swimming abilities.
By incorporating targeted exercises, you can enhance your upper body strength and endurance, ultimately enhancing your swimming performance.
Core Muscles
Swimming engages multiple muscle groups, and one of the key areas involved is the core. The abdominals play a crucial role in swimming, providing stability and support throughout the stroke.
In addition to the main abdominal muscles, the obliques also come into play, helping to maintain stability and control as you move through the water.
Strengthening these muscles is important for swimmers, as it improves their form and helps prevent injuries. Another set of muscles essential for swimming is the lower back muscles.
These muscles work with the abdominals to ensure proper body alignment and a streamlined position in the water.
By strengthening the lower back, swimmers can enhance their swimming efficiency and reduce the risk of back pain. The core muscles are vital for a strong and effective swimming technique.
Different swimming strokes activate various muscle groups. Explore the benefits of swimming breaststroke to understand its unique muscle engagement and advantages.
Lower Body Muscles
Swimming engages several muscles in the lower body for propulsion and power. The legs are pivotal as they generate the force to move through the water efficiently.
Strong glutes are essential for a powerful kick, propelling the swimmer forward.
Quadriceps and hamstrings are also vital in swimming, providing stability and balance while in the water. These muscles enable the legs to execute movements such as the flutter kick and breaststroke kick.
Strengthening the quadriceps and hamstrings enhances overall swimming performance and helps prevent injuries.
Proper technique and regular training are essential for optimizing the use of these lower body muscles in swimming.
So, focusing on exercises that target and strengthen these muscles can greatly benefit swimmers, improving their speed and endurance in the water.
Technique and Muscle Engagement
Swimming relies on various muscles throughout the body to propel through the water. Proper technique is crucial for optimal muscle engagement. Different strokes target specific muscle groups, enabling a comprehensive workout.
You can target different muscle groups and ensure balanced strength development by incorporating various swim workouts into your routine.
Variation in workouts promotes overall muscle engagement, as different muscles are activated to perform different strokes.
Whether it’s the core muscles engaged during the butterfly stroke or the leg muscles utilized in the breaststroke, each swim stroke offers unique benefits.
So, by understanding the techniques and muscle engagement involved, you can customize your swimming workouts to target specific muscle groups and enhance overall fitness effectively.
Cross Training for Swimmers
Swimming engages various muscle groups for a full-body workout. Cross-training can further enhance a swimmer’s performance by incorporating strength training exercises.
Cardiovascular exercises such as running or cycling help complement swimming by improving overall endurance. Stretching and flexibility exercises are vital for muscle recovery and reducing the risk of injuries.
These exercises help increase the range of motion in the muscles used during swimming, enabling swimmers to move more efficiently in the water.
By including strength training and cardiovascular exercises in their routine, swimmers can build muscle strength, improve endurance, and enhance their swimming performance.
Incorporating a well-rounded training program that targets different muscle groups and focuses on cardiovascular fitness and flexibility will undoubtedly contribute to a swimmer’s success in the pool.
Freestyle is one of the most popular swimming strokes. Discover what muscles freestyle swimming works and how it contributes to a full-body workout.
Injury Prevention and Muscle Conditioning
Swimming engages various muscles, including the arms, shoulders, back, abdominals, and legs. Injury prevention is crucial for swimmers to maintain muscle health.
Common swim-related injuries can be prevented by strengthening exercises targeting all muscle groups. It is important to address and correct any muscle imbalances to reduce the risk of injury.
Rest and recovery play a vital role in maintaining muscle health. Giving the muscles time to recover and repair themselves is essential to prevent overuse injuries.
By focusing on injury prevention, muscle conditioning, and incorporating proper rest and recovery, swimmers can keep their muscles strong and healthy for optimal performance in the water.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Muscles Are Used When Swimming?
Swimming primarily engages the muscles in your arms, shoulders, back, core, and legs.
How Does Swimming Help Strengthen Muscles?
Swimming is a low-impact workout that targets multiple muscle groups, promoting strength and flexibility.
Can Swimming Tone Your Muscles?
Yes, swimming is an excellent way to tone and sculpt your muscles while improving cardiovascular fitness.
Does Swimming Build Arm Muscles?
Swimming involves repetitive arm movements, which helps to build and strengthen your arm muscles over time.
What Are the Benefits of Swimming for Muscle Development?
Swimming increases muscle endurance, promotes balanced muscle development, and can aid in weight loss.
Conclusion
Swimming is a full-body workout that engages various muscle groups, making it an excellent exercise for overall strength and fitness.
By understanding the muscles used in swimming, you can optimize your training and improve your performance in the water.
When you’re swimming freestyle, your arms and shoulders play a major role in propulsion, while your core muscles provide stability and power as you rotate your body.
The muscles of your legs, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves, help generate the kicking motion that propels you forward.
Your back muscles, including the latissimus dorsi and trapezius, are engaged as you pull your arms through the water.
It’s important to note that swimming targets muscles that are often underutilized in other forms of exercise, making it a great way to maintain overall muscle balance and prevent muscle imbalances or injuries.
Regular swimming can also help improve cardiovascular fitness, increase lung capacity, and enhance flexibility.
So, whether you’re a beginner or an advanced swimmer, understanding the muscles used in swimming can help you design a more effective workout routine and maximize the benefits of this low-impact, high-intensity exercise.